The fifth generation of wireless technology, commonly known as 5G, is rapidly transforming our digital landscape. Unlike previous generations that brought incremental improvements, 5G represents a quantum leap in connectivity capabilities that will reshape how businesses operate and consumers interact with technology.
Understanding 5G Technology
5G operates on three different spectrum bands, each with unique characteristics and applications:
- Low-band spectrum – Offers wide coverage area but with peak speeds of about 100 Mbps
- Mid-band spectrum – Balances coverage and speed with peak speeds up to 1 Gbps
- High-band spectrum (mmWave) – Delivers the highest performance (up to 10 Gbps) but with limited coverage area
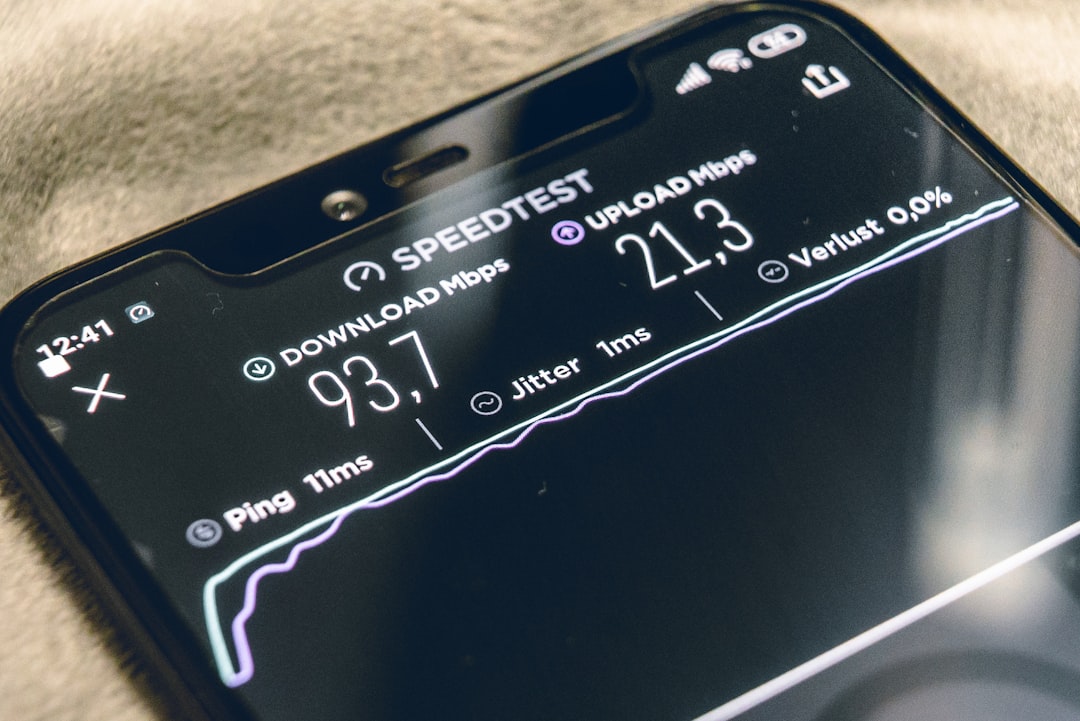
This multi-band approach enables 5G to deliver significantly higher data rates, reduced latency, massive network capacity, and a more uniform user experience compared to 4G LTE. The technical improvements include:
- Peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps
- Latency as low as 1 millisecond
- Capacity for up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer
- Network reliability of 99.999%
Transformative Applications of 5G
Enhanced Mobile Broadband
The most immediate and noticeable impact of 5G is dramatically faster mobile internet speeds. Consumers can download movies in seconds rather than minutes, enjoy seamless 4K and 8K video streaming, and experience immersive AR and VR applications without lag or buffering. This enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) capability opens new possibilities for media consumption, remote work, and digital entertainment.
Industrial IoT and Smart Manufacturing
5G's ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) capability makes it ideal for industrial applications. Manufacturing facilities are implementing 5G private networks to enable real-time monitoring and control of equipment, predictive maintenance, autonomous robots, and digital twins. These technologies are driving a new era of smart manufacturing that promises increased efficiency, productivity, and flexibility.

Healthcare Revolution
In healthcare, 5G is enabling remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and even remote surgery. The combination of high bandwidth and low latency allows for real-time transmission of high-definition medical images and videos, while also supporting the deployment of connected medical devices. This technology is particularly valuable for providing healthcare services to underserved rural communities.
Autonomous Vehicles
The development of autonomous vehicles relies heavily on fast, reliable connectivity. 5G provides the low-latency communication necessary for vehicles to interact with each other and with road infrastructure in real-time. This vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication enables safer navigation, traffic optimization, and ultimately fully autonomous driving.
Smart Cities
5G is foundational for smart city initiatives, supporting massive machine-type communications (mMTC) for thousands of connected devices. Applications include intelligent traffic management, energy-efficient street lighting, environmental monitoring, and public safety enhancements. These connected urban environments can significantly improve quality of life while reducing resource consumption.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its transformative potential, 5G deployment faces several challenges:
Infrastructure Requirements
The high-frequency spectrum used by 5G requires a denser network of small cells, which means significant infrastructure investment. Urban areas will likely see faster deployment, potentially widening the digital divide with rural regions unless specific strategies are implemented to address coverage in less populated areas.
Security Concerns
The expanded attack surface created by the massive number of connected devices raises new security challenges. Network security must evolve to protect against more sophisticated threats while maintaining the performance benefits of 5G. End-to-end encryption, network slicing, and enhanced authentication mechanisms are being implemented to address these concerns.
Energy Consumption
The power requirements for 5G infrastructure are higher than previous generations, raising questions about environmental sustainability. The industry is working on energy-efficient hardware and intelligent power management systems to minimize the carbon footprint of 5G networks.
The Future of Connectivity
As 5G continues to roll out globally, we're just beginning to see its full potential. The technology will enable new business models, create new industries, and fundamentally change how we interact with technology. Some key trends to watch include:
- The convergence of 5G with other technologies like AI, edge computing, and blockchain
- The development of application-specific network slices tailored to different industry needs
- New immersive entertainment experiences combining 5G, AR/VR, and cloud gaming
- Innovative IoT applications that weren't previously possible due to connectivity limitations
5G represents more than just faster mobile internet; it's a platform for innovation that will drive digital transformation across industries and society. As the technology matures and becomes more widely available, we'll continue to discover new applications and use cases that redefine what's possible in our connected world.